在中已经对Draw2D进行了一些概要介绍,本篇从一个流程图的编写来学习Draw2D的是GEF的基础。
练习要求
做一个图下图所示流程图,流程图中的各个图例可以移动,每个不同类型的图例也不一样。 源码下载:

基础概念
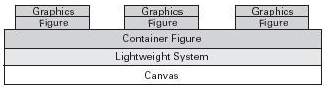
图例Figure
这里支持三种图例,图例从ActivityFigure继承下来。主要就是画图还有定义连接点FixedAnchor,下面先看看代码,代码都比较简单
- 开始、结束图例
public class TerminatorFigure extends ActivityFigure { FixedAnchor inAnchor, outAnchor; public TerminatorFigure() { inAnchor = new FixedAnchor(this); inAnchor.place = new Point(1, 0); targetAnchors.put("in_term", inAnchor); outAnchor = new FixedAnchor(this); outAnchor.place = new Point(1, 2); sourceAnchors.put("out_term", outAnchor); } public void paintFigure(Graphics g) { Rectangle r = bounds; g.drawArc(r.x + r.width / 8, r.y, r.width / 4, r.height - 1, 90, 180); g.drawLine(r.x + r.width / 4, r.y, r.x + 3 * r.width / 4, r.y); g.drawLine(r.x + r.width / 4, r.y + r.height - 1, r.x + 3 * r.width / 4, r.y + r.height - 1); g.drawArc(r.x + 5 * r.width / 8, r.y, r.width / 4, r.height - 1, 270, 180); g.drawText(message, r.x + 3 * r.width / 8, r.y + r.height / 8); }} - 分支图例
public class DecisionFigure extends ActivityFigure { FixedAnchor inAnchor, yesAnchor, noAnchor; public DecisionFigure() { inAnchor = new FixedAnchor(this); inAnchor.place = new Point(1, 0); targetAnchors.put("in_dec", inAnchor); noAnchor = new FixedAnchor(this); noAnchor.place = new Point(2, 1); sourceAnchors.put("no", noAnchor); yesAnchor = new FixedAnchor(this); yesAnchor.place = new Point(1, 2); sourceAnchors.put("yes", yesAnchor); } public void paintFigure(Graphics g) { Rectangle r = bounds; PointList pl = new PointList(4); pl.addPoint(r.x + r.width / 2, r.y); pl.addPoint(r.x, r.y + r.height / 2); pl.addPoint(r.x + r.width / 2, r.y + r.height - 1); pl.addPoint(r.x + r.width, r.y + r.height / 2); g.drawPolygon(pl); g.drawText(message, r.x + r.width / 4 + 5, r.y + 3 * r.height / 8); g.drawText("N", r.x + 7 * r.width / 8, r.y + 3 * r.height / 8); g.drawText("Y", r.x + r.width / 2 - 2, r.y + 3 * r.height / 4); }} - 流程图例
public class ProcessFigure extends ActivityFigure { FixedAnchor inAnchor, outAnchor; public ProcessFigure() { inAnchor = new FixedAnchor(this); inAnchor.place = new Point(1, 0); targetAnchors.put("in_proc", inAnchor); outAnchor = new FixedAnchor(this); outAnchor.place = new Point(1, 2); sourceAnchors.put("out_proc", outAnchor); } public void paintFigure(Graphics g) { Rectangle r = bounds; g.drawText(message, r.x + r.width / 4, r.y + r.height / 4); g.drawRectangle(r.x, r.y, r.width - 1, r.height - 1); }} - FixedAnchor:连接画线时会根据place来调用getLocation确定连接终点的位置
public class FixedAnchor extends AbstractConnectionAnchor{ Point place; public FixedAnchor(IFigure owner) { super(owner); } public Point getLocation(Point loc) { Rectangle r = getOwner().getBounds(); int x = r.x + place.x * r.width/2; int y = r.y + place.y * r.height/2; Point p = new PrecisionPoint(x,y); getOwner().translateToAbsolute(p); return p; }} - ActivityFigure:主要处理连接点的代码
abstract public class ActivityFigure extends Figure { Rectangle r = new Rectangle(); Hashtable targetAnchors = new Hashtable(); Hashtable sourceAnchors = new Hashtable(); String message = new String(); public void setName(String msg) { message = msg; repaint(); } public ConnectionAnchor ConnectionAnchorAt(Point p) { ConnectionAnchor closest = null; long min = Long.MAX_VALUE; Hashtable conn = getSourceConnectionAnchors(); conn.putAll(getTargetConnectionAnchors()); Enumeration e = conn.elements(); while (e.hasMoreElements()) { ConnectionAnchor c = (ConnectionAnchor) e.nextElement(); Point p2 = c.getLocation(null); long d = p.getDistance2(p2); if (d < min) { min = d; closest = c; } } return closest; } public ConnectionAnchor getSourceConnectionAnchor(String name) { return (ConnectionAnchor) sourceAnchors.get(name); } public ConnectionAnchor getTargetConnectionAnchor(String name) { return (ConnectionAnchor) targetAnchors.get(name); } public String getSourceAnchorName(ConnectionAnchor c) { Enumerationkeys = sourceAnchors.keys(); String name; while (keys.hasMoreElements()) { name = (String) keys.nextElement(); if (sourceAnchors.get(name).equals(c)) return name; } return null; } public String getTargetAnchorName(ConnectionAnchor c) { Enumeration keys = targetAnchors.keys(); String name = null; while (keys.hasMoreElements()) { name = (String) keys.nextElement(); if (targetAnchors.get(name).equals(c)) return name; } return null; } public ConnectionAnchor getSourceConnectionAnchorAt(Point p) { ConnectionAnchor closest = null; long min = Long.MAX_VALUE; Enumeration e = getSourceConnectionAnchors().elements(); while (e.hasMoreElements()) { ConnectionAnchor c = (ConnectionAnchor) e.nextElement(); Point p2 = c.getLocation(null); long d = p.getDistance2(p2); if (d < min) { min = d; closest = c; } } return closest; } public Hashtable getSourceConnectionAnchors() { return sourceAnchors; } public ConnectionAnchor getTargetConnectionAnchorAt(Point p) { ConnectionAnchor closest = null; long min = Long.MAX_VALUE; Enumeration e = getTargetConnectionAnchors().elements(); while (e.hasMoreElements()) { ConnectionAnchor c = (ConnectionAnchor) e.nextElement(); Point p2 = c.getLocation(null); long d = p.getDistance2(p2); if (d < min) { min = d; closest = c; } } return closest; } public Hashtable getTargetConnectionAnchors() { return targetAnchors; }}
连接点PathFigure
连接点从PolylineConnection继承下来,在构造函数中设置目标对象连接点的装饰类,也就是示例中的三角形(PolylineDecoration),以及设定连接线路由样式,这里设置为ManhattanConnectionRouter
public class PathFigure extends PolylineConnection { public PathFigure() { //setSourceDecoration(new PolygonDecoration()); setTargetDecoration(new PolylineDecoration()); //setConnectionRouter(new BendpointConnectionRouter()); setConnectionRouter(new ManhattanConnectionRouter()); }} 监听移动事件
public class Dnd extends MouseMotionListener.Stub implements MouseListener { public Dnd(IFigure figure) { figure.addMouseMotionListener(this); figure.addMouseListener(this); } Point start; public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) { } public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) { } public void mouseDoubleClicked(MouseEvent e) { } public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) { start = e.getLocation(); } public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) { Point p = e.getLocation(); Dimension d = p.getDifference(start); start = p; Figure f = ((Figure) e.getSource()); f.setBounds(f.getBounds().getTranslated(d.width, d.height)); }}
Flowchart
Flowchart是主程序代码,生成最上图所示的所有图例、连接,并把连接于连接点关联起来,并加入监听移动事件对象
public class Flowchart { public static void main(String args[]) { Shell shell = new Shell(); shell.setSize(300, 400); shell.open(); shell.setText("Flowchart"); LightweightSystem lws = new LightweightSystem(shell); ChartFigure flowchart = new ChartFigure(); lws.setEventDispatcher(new SWTEventDispatcherX(1800000L)); lws.setContents(flowchart); TerminatorFigure start = new TerminatorFigure(); start.setName("Start"); start.setToolTip(new Label("起点")); start.setBounds(new Rectangle(40, 20, 80, 20)); DecisionFigure dec = new DecisionFigure(); dec.setName("Should I?"); dec.setBounds(new Rectangle(30, 60, 100, 60)); ProcessFigure proc = new ProcessFigure(); proc.setName("Do it!"); proc.setToolTip(new Button("do it")); proc.setBounds(new Rectangle(40, 140, 80, 40)); TerminatorFigure stop = new TerminatorFigure(); stop.setName("End"); stop.setBounds(new Rectangle(140, 300, 80, 20)); PathFigure path1 = new PathFigure(); path1.setSourceAnchor(start.outAnchor); path1.setTargetAnchor(dec.inAnchor); PathFigure path2 = new PathFigure(); path2.setSourceAnchor(dec.yesAnchor); path2.setTargetAnchor(proc.inAnchor); PathFigure path3 = new PathFigure(); path3.setSourceAnchor(dec.noAnchor); path3.setTargetAnchor(stop.inAnchor); PathFigure path4 = new PathFigure(); path4.setSourceAnchor(proc.outAnchor); path4.setTargetAnchor(stop.inAnchor); flowchart.add(start); flowchart.add(dec); flowchart.add(proc); flowchart.add(stop); flowchart.add(path1); flowchart.add(path2); flowchart.add(path3); flowchart.add(path4); new Dnd(start); new Dnd(proc); new Dnd(dec); new Dnd(stop); Display display = Display.getDefault(); while (!shell.isDisposed()) { if (!display.readAndDispatch()) display.sleep(); } }}
参考:
推荐:
欢迎转载,转载请注明:转载自 [ ]